It's a production technology that uses the power of ordinary or special stamping equipment to make metal sheets deform directly under the force in the molds, so as to get metal sheet products with specific shapes and specifications. It's only suitable for product types that are relatively single in variety, have a large production volume, are small in structure, and are relatively stable.

(1) Material Selection: Choose suitable sheet metal materials according to factors like the usage requirements, performance characteristics, and cost of the products. Common materials include iron plates, stainless steel, aluminum, and aluminum alloys.
(2) Material Inspection: Inspect the purchased raw materials. Check if the specifications (such as thickness, width, length, etc.) of the materials meet the requirements and if there are any scratches, oxide layers, dents, etc. on the surface. At the same time, test the mechanical properties of the materials, like tensile strength and yield strength, to make sure the material quality is okay and can meet the needs of the stamping process.
(3) Material Cutting: Cut the large metal sheets according to the size requirements of the stamping parts to get blanks of the right size. You can use equipment like shearing machines for cutting. During the cutting process, make sure the dimensional accuracy of the blanks is ensured to provide a good foundation for the following stamping steps.
(1) Part Analysis: Analyze the parts to be stamped in detail, including their shape, dimensional accuracy, surface quality requirements, and batch size.
(2) Formulation of Process Plan: Based on the results of the part analysis, make a stamping process plan. Decide the order of the stamping steps, like whether to punch holes first and then bend, or to stretch first and then punch holes. At the same time, choose suitable stamping equipment and consider if parameters such as the tonnage, stroke, and worktable size of the equipment can meet the process requirements.
(3) Die Design: The die is a key tool in sheet metal stamping. Design the stamping die according to the process plan. Die design includes the design of the die structure (such as single-operation dies, compound dies, progressive dies, etc.) and the design of die parts (such as punch, die, stripper plate, etc.). Make sure the die can accurately process the blanks into the required part shapes and has enough strength and a long service life.
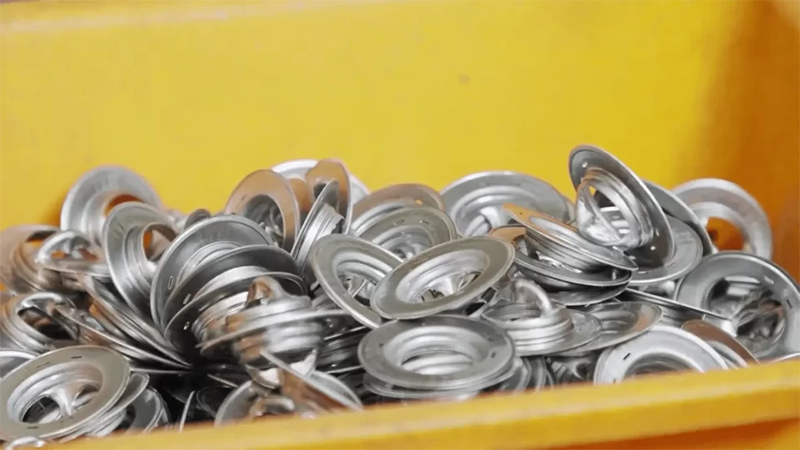

(1) Installation of Dies: Install the designed dies on the stamping equipment, adjust the position and clearance of the dies to make sure they are installed correctly. During the installation process, strictly follow the installation instructions of the equipment and dies to ensure that the upper and lower dies are aligned and the clearance is uniform.
(2) First Article Trial Stamping: Before starting the formal mass production, do a first article trial stamping. Through this trial stamping, you can check if the installation of the dies is correct, if the stamping process parameters are reasonable, and if the shape and size of the parts meet the design requirements. If there are any problems, adjust the dies or process parameters in time.
(3) Mass Stamping: After the first article trial stamping is qualified, start the mass stamping production. During the stamping process, control the stamping speed, pressure, and other process parameters to ensure the quality of each part is stable. At the same time, the operators should pay attention to observing the operation conditions of the equipment and dies and promptly discover and handle abnormal situations like die wear and equipment failure.
(1) Appearance Inspection: Do an appearance inspection on the stamped parts to check if there are any scratches, cracks, folds, etc. on the surface of the parts. The appearance quality directly affects the beauty and performance of the product. For some parts with surface quality requirements, like the outer covering parts of a car body or the shells of electronic products, the appearance inspection is especially important.
(2) Dimensional Accuracy Detection: Use measuring tools like calipers, micrometers, and coordinate measuring machines to detect the dimensions of the parts and check if the dimensions of the parts are within the tolerance range of the design requirements. Dimensional accuracy is an important indicator to measure the quality of stamping parts. Any dimensional deviation may cause the part to be unable to be assembled or used normally.
(3) Performance Testing: According to the usage requirements of the parts, do relevant performance tests. For example, for sheet metal parts that bear pressure, do a pressure test; for parts with conductivity requirements, do a conductivity test. Through performance tests, it can be ensured that the parts meet the actual performance requirements of use.
(1) Deburring: During the stamping process, burrs may appear on the edges of the parts. These burrs not only affect the appearance of the parts but also may have an impact on the assembly or use of the parts. You can use tools or equipment like files, sandpaper, and deburring machines to remove the burrs on the edges of the parts.
(2) Surface Treatment: According to the requirements of the product, do surface treatment on the stamped parts. Common surface treatment methods include painting, electroplating, anodic oxidation, etc. Surface treatment can improve the corrosion resistance and beauty of the parts.
(3) Part Assembly: The stamped parts after quality inspection and subsequent treatment can be assembled. Assemble multiple parts into the final product. During the assembly process, follow the assembly process requirements to ensure the assembly quality of the product.
Sheet metal stamping is a very important manufacturing process widely used in various industries. This process is very useful for many industries as it helps to produce simple and complex components or parts at the most affordable prices. It can produce products ranging from simple components to complex components.