Sheet Metal Processing, as the name suggests, involves using metal sheets to create desired items based on requirements. Common items made from metal sheets include computer cases and cabinets, television back panels, car bodies, air conditioner housings, terminal integrated machine shells, and charging pile boxes.
Sheet Metal Processing primarily involves processes such as cutting and blanking, CNC bending, punching, shearing, rolling, riveting, and welding. It can also refer to the working principles and operation methods of various equipment.
All sheet metal processing techniques require meticulous design and specification marking by a sheet metal engineer before operation.
Main process terms include: blanking, riveting, bending, shearing, punching, extrusion, tapping, riveting, crimping, corner cutting, forming, punching convex packets, breaking, imprinting, reaming, perforating, chamfering, threading, hole drawing, tapping, flattening, welding, spraying, and assembly.
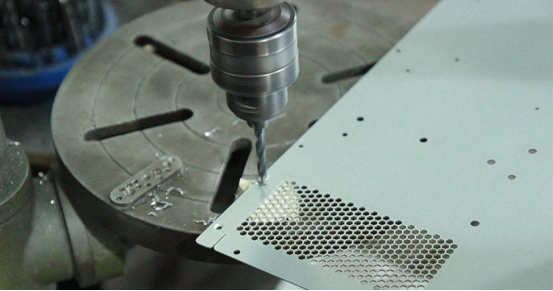
Sheet Metal Processing: Laser Blanking
There are various blanking methods, which involve processing workpieces through laser cutting or CNC punching, shearing. NC CNC blanking and laser cutting blanking can be used for processing thicker and more complex sheet metal pieces; shearing can produce larger external dimensions of workpieces; punching can mass-produce workpiece shapes and holes using a punch.
Sheet Metal Processing: Copper Bar Punching
Hole drawing, also called flanging, involves using a die on a common punch or other punching equipment to create a specified size hole on a pre-punched piece. This process imparts more strength to the threads on the workpiece, generally used for workpieces with a thickness below1.5mm.
Sheet Metal Processing: Riveting
This typically involves the process of using a punch or hydraulic riveting machine to firmly rivet and press connectors such as rivet studs, rivet nuts, and rivet screws onto the workpiece.
Sheet Metal Processing: CNC Bending
Bending involves using a press brake and related bending dies to form the workpiece on a bending machine, enhancing the strength of the processed workpiece.
Sheet Metal Welding
Common welding types include CO2 welding, argon arc welding, electric welding, robotic welding, and spot welding. These processes mainly involve welding two or more parts together to achieve finished products or assembly purposes. It may also refer to welding seams on single parts to precision, enhancing bending strength.
Surface Treatment
Surface treatments include phosphating membrane spraying, electroplating with colorful zinc, chromate, baking paint, oxidation, etc.. Phosphating membrane allows for electrostatic powder spraying suitable for cold-rolled steel and galvanized plates; colorful zinc electroplating is typically used for cold-rolled steel and machined parts; chromate and oxidation treatments are generally used for aluminum and aluminum profiles. Surface treatments aim to enhance the appearance and protect sheet metal parts, with specific methods determined by customer material requirements.
Assembly
This involves assembling multiple parts or components according to drawings into a complete workpiece product. The assembled workpiece can be a finished product or a semi-finished product.