Die casting is a metal casting process characterized by applying high pressure to the molten metal through the mold cavity. The mold is usually made of a stronger alloy, and the process is somewhat similar to injection molding. Most die castings are non-ferrous, such as zinc, copper, aluminum, magnesium, lead, tin, lead-tin alloys and their alloys. Depending on the type of die casting, a cold chamber die casting machine or a hot chamber die casting machine is required.
Casting equipment and molds are expensive, so the die casting process is generally only used to batch manufacture a large number of products. It is relatively easy to manufacture die-cast parts, which generally requires only four main steps and the unit cost increment is very low. Die casting is particularly suitable for manufacturing a large number of small and medium-sized castings, so die casting is the most widely used of various casting processes. Compared with other casting technologies, die casting has a flatter surface and higher dimensional consistency.
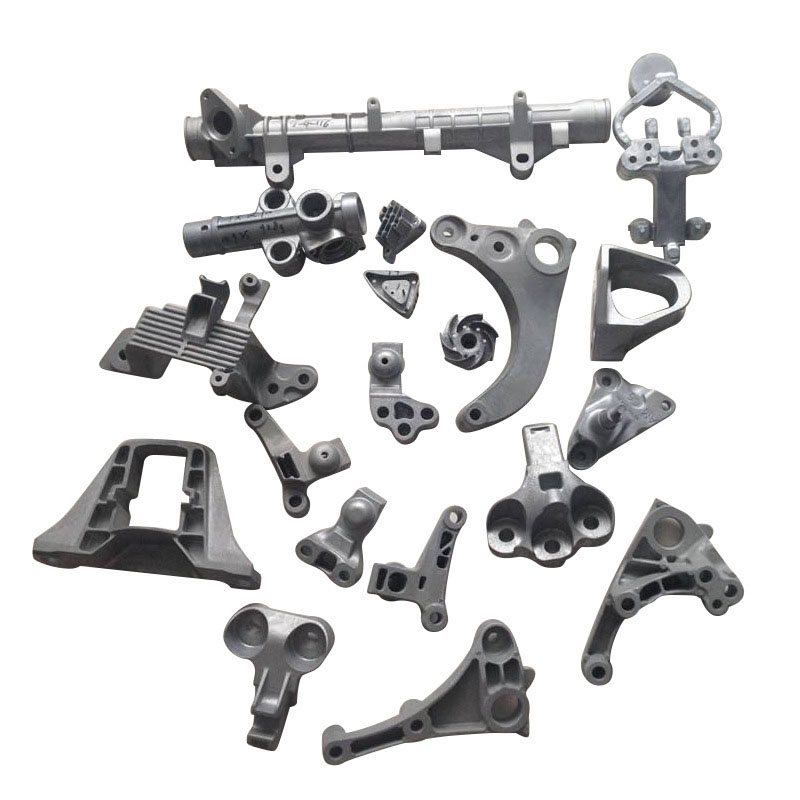

The die casting process is suitable for mass production of parts with complex shapes and precision requirements, such as automotive parts, electronic product housings, home appliance components, etc.
Mold design and manufacturing: Make the mold according to the design drawings of the parts. The mold usually consists of two parts, namely the fixed mold and the movable mold, and high-strength steel materials are usually used.
Mold preheating: In order to ensure the quality of the casting, it is sometimes necessary to preheat the mold before die casting to improve the life of the mold and the surface quality of the casting.
Melting metal: According to the material requirements of the casting (such as aluminum, zinc, copper alloy, etc.), the metal is placed in a furnace and heated to a molten state.
Temperature control: Keep the melting temperature of the alloy within a suitable range to ensure fluidity and casting quality.
Injection device preparation: The molten metal liquid is fed into the mold through the injection system (including the nozzle, the hydraulic system of the die-casting machine, etc.).
High-speed injection: The molten metal is quickly injected into the mold cavity through the injection pressure to fill the mold and shape the desired casting shape.
Cooling and solidification: After the molten metal fills the mold, it begins to cool rapidly until it is completely solidified and formed.
Cooling time: According to the type of metal and the design of the mold, the cooling time should be properly controlled. Cooling too fast or too slow will affect the quality of the casting.
Demolding: After the metal solidifies, open the mold and remove the casting. At this time, the casting usually still maintains a certain temperature.
Removing overflow: There is usually excess casting on the surface of the casting, which needs to be removed by trimming, such as removing the gate, runner, etc.
Surface treatment: If necessary, post-processing processes such as surface grinding, spraying, and polishing can be performed to improve the appearance and performance.
Appearance inspection: Check whether there are defects on the surface of the casting, such as pores, cracks, etc.
Dimension inspection: The dimension of the casting is checked by precision measuring tools to ensure that it meets the design requirements.
Mechanical property testing: Sometimes it is necessary to perform mechanical property tests on the casting, such as tensile and hardness tests, to ensure its strength and durability.
Finishing: Some castings may require further processing, such as cutting, drilling, milling, etc., to meet the use requirements.
Heat treatment: Depending on the needs, some castings may also require heat treatment (such as aging, quenching, etc.) to improve material properties.
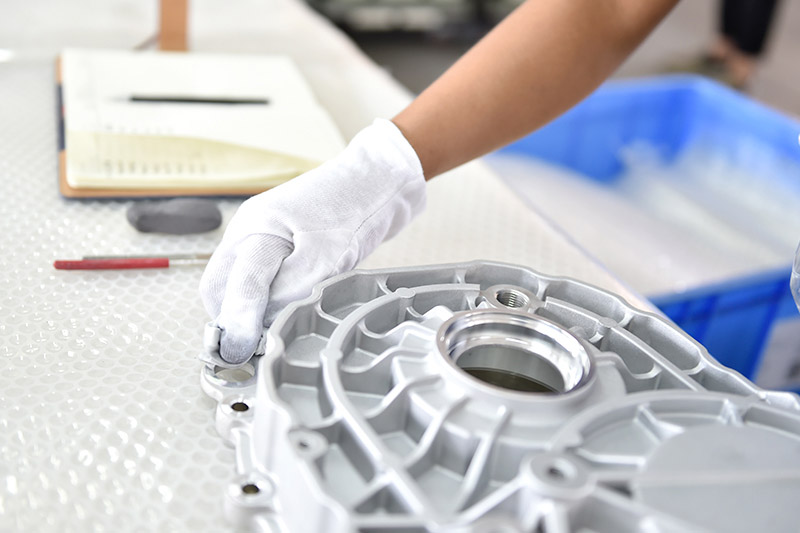

The casting has high dimensional accuracy, generally equivalent to level 6~7, or even level 4; good surface finish, generally equivalent to level 5~8; high strength and hardness, the strength is generally 25~30% higher than sand casting, but the elongation is reduced by about 70%; stable dimensions and good interchangeability; can die-cast thin-walled and complex castings. For example, the current minimum wall thickness of zinc alloy die castings can reach 0.3mm; aluminum alloy castings can reach 0.5mm; the minimum cast hole diameter is 0.7mm; the minimum pitch is 0.75mm.
The machine has high productivity. For example, the domestic JⅢ3 horizontal cold air die-casting machine can die-cast 600 to 700 times in eight hours on average, and the small hot chamber die-casting machine can die-cast 3,000 to 7,000 times every eight hours on average; the die-casting mold has a long life, and a pair of die-casting molds, die-casting bell alloy, can have a life of hundreds of thousands of times, or even millions of times; it is easy to realize mechanization and automation.
Due to the advantages of precise size and smooth surface of die-casting parts. Generally, they are used directly without mechanical processing, or the processing volume is very small, so the metal utilization rate is improved, and a large amount of processing equipment and working hours are reduced; the casting price is cheap; combined die-casting can be used with other metals or non-metallic materials. It saves both assembly time and metal.
Although die-casting has many advantages, it also has some disadvantages that need to be solved.
1. During die casting, the liquid metal fills the cavity at a high speed and the flow state is unstable, so the general die casting method is used. The casting is prone to pores and cannot be heat treated;
2. Die casting is more difficult for castings with complex inner concave;
3. For high melting point alloys (such as copper, ferrous metals), the die casting mold life is relatively low;
4. It is not suitable for small batch production. The main reason is that the die casting mold manufacturing cost is high, the die casting machine production efficiency is high, and small batch production is not economical.