A junction box is a protective enclosure designed to house and organize electrical connections, wiring, and components. In metal parts fabrication, it serves as a centralized location for multiple connections, ensuring that wires and cables are safely and securely connected. Junction boxes are particularly important in industrial, commercial, and residential electrical systems, providing a shield against external elements and minimizing the risk of electrical shorts or fires.
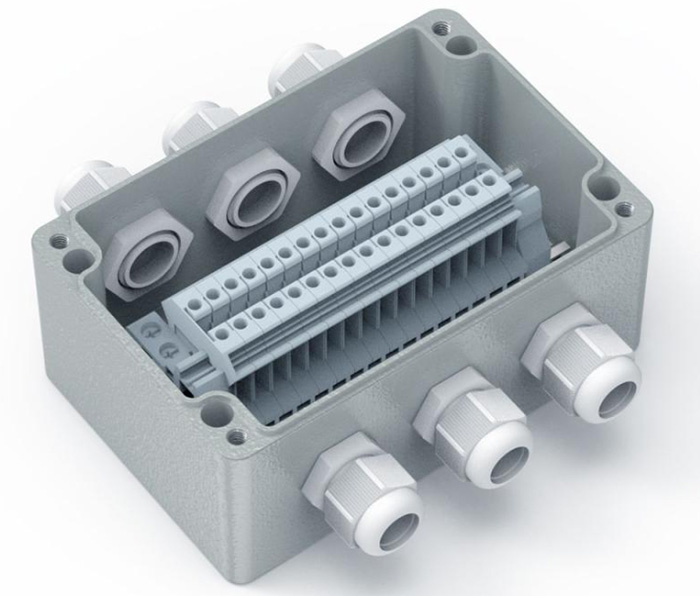
The primary function of a junction box is to protect electrical connections and prevent damage caused by external factors like moisture, dust, or physical impacts. The electric junction box is specifically designed to house electrical connections, offering protection to wires, terminals, and splices. This is crucial in maintaining the integrity of the electrical system, especially in environments where equipment is subject to harsh conditions.
Junction boxes come in various shapes, sizes, and materials. Some common types include:
Surface-mounted Junction Boxes: These are fixed to the surface of walls or ceilings and are often used for systems requiring easy access.
Flush-mounted Junction Boxes: These are embedded in the wall, creating a more aesthetically pleasing and space-efficient solution.
Explosion-proof Junction Boxes: Used in hazardous environments where there is a risk of sparks or flammable materials, these boxes are specially designed to prevent ignition.
In metal parts fabrication, junction boxes are an integral part of ensuring proper electrical connections between various components. The junction box connection involves linking wires or cables to terminals, allowing for an organized flow of electricity. The design of the junction box ensures that these connections remain stable, insulated, and safe, preventing issues like shorts, power loss, or interference.
Cable Entry and Exit Points: These points must be carefully designed to maintain safety and prevent accidental disconnections.
Internal Wiring and Terminals: A well-designed junction box offers clear and accessible wiring configurations that make it easier to troubleshoot or modify systems when needed.
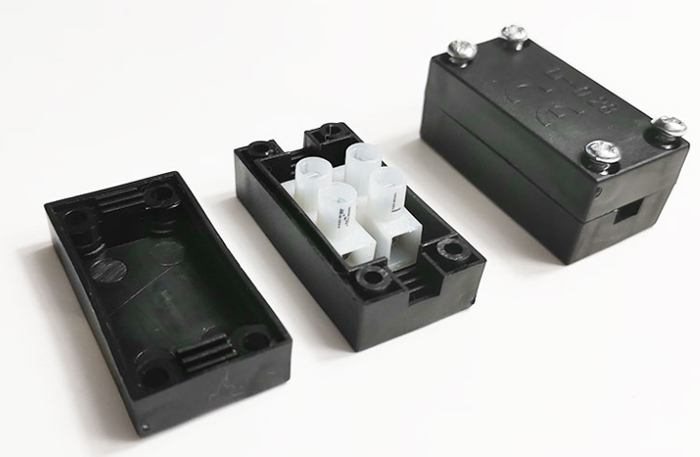

The materials used in junction box fabrication depend on the environment and specific requirements of the application. For instance, metal junction boxes are often made from durable materials such as steel, aluminum, or galvanized steel, providing robust protection against mechanical stress, corrosion, and fire hazards.
Corrosion Resistance: Metal junction boxes are especially preferred in environments with high humidity or exposure to chemicals.
Heat Resistance: Metal boxes are also ideal for high-temperature environments where plastic might degrade.
In some industries, off-the-shelf junction boxes do not meet specific requirements, necessitating custom fabrication. Manufacturers can create custom metal boxes tailored to unique specifications, such as size, mounting options, or special openings for connections. This ensures that the junction box integrates seamlessly into the system and performs optimally.
When designing or selecting junction boxes for industrial applications, adherence to safety standards is crucial. These standards, such as UL (Underwriters Laboratories) certification, ensure that the junction box can withstand electrical faults, heat, and mechanical impact without posing any hazards.
Sealing and Insulation: A good junction box should have proper seals and insulation to prevent contact with live wires and reduce the risk of electrical accidents.
Compliance with Regulations: Compliance with local or international regulations ensures the junction box meets safety requirements and is fit for the intended application.